Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a serious condition that affects millions of people worldwide, yet it often goes undiagnosed until significant damage has occurred. It's vital to recognize the signs and symptoms early to prevent further complications. Understanding what CKD entails, its causes, and exploring treatment options can empower individuals to take control of their health.
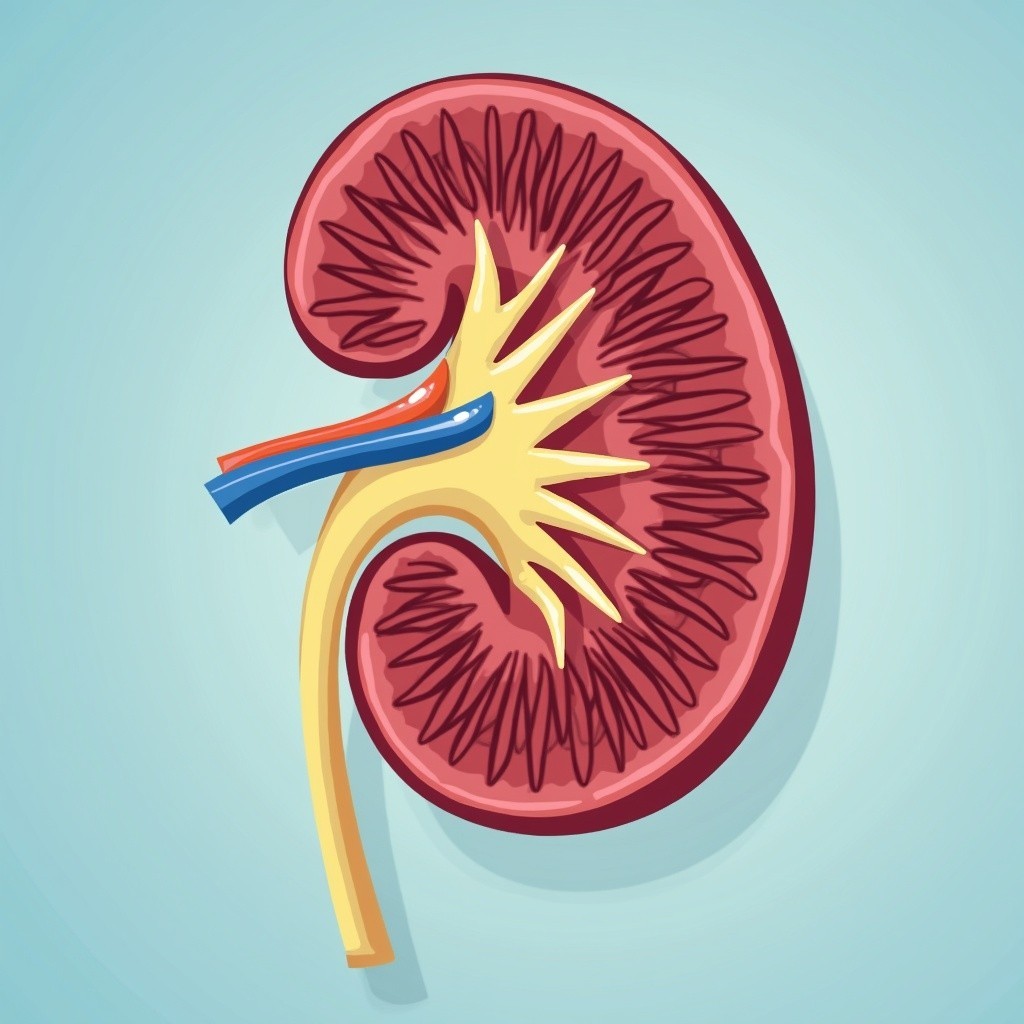
What is Chronic Kidney Disease?
Chronic Kidney Disease is a long-term health condition where the kidneys gradually lose their function over time. The kidneys, two bean-shaped organs located in the lower back, are responsible for filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, which are then excreted through urine. CKD occurs when this filtering capability diminishes, leading to the accumulation of waste products in the body, potentially causing critical health issues.
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), CKD is categorized into five stages, determined by the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which is the measurement of kidney function. A decrease in GFR indicates progressing kidney damage, and the fifth stage, known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), requires dialysis or a kidney transplant to sustain life.
Understanding the severity and progression of CKD is critical for addressing its impact and exploring effective management strategies for those affected.
Causes and Risks of Chronic Kidney Disease
The onset of CKD cannot be traced to a single cause; rather, it is often a culmination of various health conditions. Two of the primary culprits are diabetes and hypertension. Research from the Mayo Clinic indicates that high blood sugar levels in diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, while high blood pressure can cause scarring over time, impairing kidney function.
Other potential risk factors include:
- Heart Disease: Cardiovascular conditions can alter blood flow and pressure, impacting kidney health.
- Glomerulonephritis: This inflammation of kidney filtering units can lead to long-term damage.
- Polycystic Kidney Disease: A genetic disorder that leads to the growth of cysts that can replace kidney tissue over time.
- Repeated Urinary Infections: These can cause scarring and functional impairment of the kidneys.
- Family History: If kidney disease runs in the family, the risk may be higher.
- Obesity and Poor Lifestyle: Unhealthy habits, such as smoking, can exacerbate risks due to increased strain on bodily systems.
Identifying these risk factors can aid in prevention and early intervention, minimizing the impact of CKD.
Signs and Symptoms of Chronic Kidney Disease
CKD is notorious for being an insidious condition. During its early stages, symptoms might be virtually invisible. However, as the disease progresses, various signs begin to manifest. These include but are not limited to:
- Fatigue and Weakness: As toxins accumulate, patients often experience persistent fatigue.
- Swelling: Due to fluid retention, especially in the legs, ankles, or feet.
- Changes in Urination: This can include increased frequency, especially at night, or darkened urine.
- Muscle Cramps: The electrolyte imbalance can cause discomfort and cramps.
- Itchy Skin: Waste buildup in the blood can lead to dryness and itchiness.
- Shortness of Breath: If fluid accumulates in the lungs, it can affect breathing.
- Poor Appetite and Nausea: Digestive symptoms due to toxin accumulation.
For a more extensive list of symptoms, you can refer to resources like 10 Signs You May Have Kidney Disease. Recognizing these symptoms early on can lead to timely medical intervention.
Finding Doctors Near You Who Treat Chronic Kidney Disease
Early and regular consultation with healthcare professionals specializing in nephrology can significantly alter the course of CKD. Nephrologists have the expertise to assess and manage kidney health, recommending appropriate interventions depending on the severity and cause of the disease.
Here are some approaches to finding qualified kidney specialists:
- Consult Your Primary Physician: Your family doctor or general practitioner is often your best resource for referrals, based on your specific health profile.
- Utilize Medical Networks: Major hospitals and health networks usually have directories listing specialists and their areas of expertise.
- Online Directories: Websites like Kidney Fund and other medical associations provide rich databases to navigate specialists in your area.
- Insurance Providers: Health insurance companies often offer lists of in-network nephrologists that match your coverage, easing the financial consideration of care.
- Word of Mouth: Personal recommendations from others with CKD experience can provide insights into where to receive the best care.
Finding a specialized doctor is a crucial step towards effective CKD management, allowing personalized treatment plans that cater to individual needs.
Treatment Options for Chronic Kidney Disease
While there's no cure for CKD, various strategies can slow its progression and alleviate symptoms, significantly improving the quality of life.
1. **Lifestyle Modifications:**
- **Dietary Changes:** Limiting sodium, potassium, and protein intake can reduce renal load. Seeking advice from a dietician specialized in renal diets is beneficial.
- **Exercise:** Regular physical activity maintains a healthy weight and blood pressure, crucial for kidney health.
- **Avoid Smoking and Alcohol:** Both can exacerbate kidney damage and complicate medical treatment.
2. **Medication:**
- **Blood Pressure Control:** Using ACE inhibitors or ARBs helps control blood pressure, slowing kidney disease.
- **Managing Diabetes:** Keeping blood glucose levels in check with medications or insulin.
- **Cholesterol Medication:** Statins can help reduce cardiovascular risks, pivotal in CKD patients.
3. **Regular Monitoring:**
- Ensuring consistent check-ups and blood tests to monitor kidney function and adapt treatment as needed.
4. **Dialysis and Transplant:**
- For those reaching ESRD, dialysis retains some kidney functions, while a transplant provides a more permanent solution, albeit with complexities like donor matching and lifelong medication.
Managing CKD is an evolving process that relies heavily on patient cooperation, medical guidance, and timely interventions. Embracing lifestyle changes and understanding the disease intricacies empower patients to take charge of their health outcomes effectively.
Understanding Chronic Kidney Disease is vital for mitigating its extensive repercussions on individuals and healthcare systems. By recognizing symptoms, knowing risks, and seeking timely treatment, those affected can navigate the challenges more adeptly, leading to improved health and life expectancy.